
The automotive industry boasts a long tradition and plays a very important role in Italy’s economic development. This is true for the entire value chain, from vehicle and component design to the manufacture and marketing of finished goods.
In particular, Italy’s unique value proposition, that is placed within a secure and safe geopolitical platform, can be summarized as follows:
 |
Strong growth platform |
 |
Fertile Automotive ecosystem |
 |
First-class talent pool |
 |
Optimal fab buildout conditions |
 |
Highly-supportive government |
INDUSTRY OUTLOOK
Italy is appreciated all over the world for its luxury brands, sports cars, design and quality of production, proving the competitiveness of its automotive industry.
Specifically, Italy is among the main producers in Europe, recording 0,78 million of motor vehicles manufactured in 2022.
 |
Sources: ISTAT (Ateco code 29); ACEA
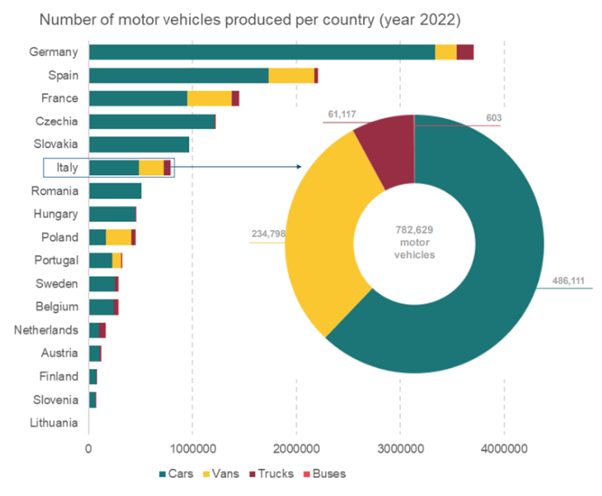 |
Source: ACEA – European Automobile Manufacturers Association
In 2022, the Italian automotive sector recorded €18 billion in the export of new vehicles, including cars and industrial vehicles (+11% vs. 2021) and €23,5 billion in the export of components (+7% vs. 2021).
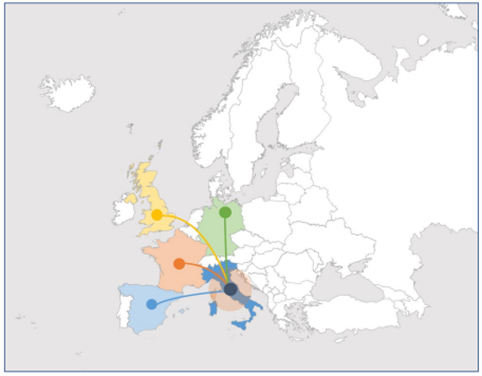
Thanks to logistical connections, foreign companies that choose Italy for their business can easily access the European automotive market, which with over 16 million motor vehicles produced, is the second large area of production in the world.
 |
The Italian automotive components ecosystem in a nutshell (year 2022):
▪ 2.167 companies
▪ €56 billion turnover
▪ 167.000 employees
▪ €23,5 billion of export
Sources: Invitalia Report 2023 on data from ISTAT; ACEA – European Automobile Manufacturers Association; Focus Italia Mercato Autovetture, February 2023, ANFIA - Italian Association of the Automotive Industry; Osservatorio sulla componentistica automotive italiana e sui servizi per la mobilità 2023 (ANFIA, Camera di Commercio di Torino); Osservatorio sulla componentistica automotive italiana 2022, ANFIA, Camera di Commercio di Torino; Ceipiemonte; Focus UE/EFTA/UK mercato autovetture ad alimentazione alternativa, FY 2022, Area Studi e Statistiche ANFIA; Connected Car&Moblity, l’andamento del mercato in Italia, 2020-2022, Osservatori Digital Innovation – Politecnico di Milano (www.osservatori.net); 7° Rapporto nazionale sulla sharing mobility, Osservatorio Nazionale Sharing Mobility, 2023; Istat NACE code 29 - Manufacture of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers; Scimago Journal & Country Rank; QS World University Rankings by Subject 2023; https://www.investintuscany.com/; https://clusterlucanoautomotive.it/; Osservatorio sulla componentistica automotive italiana 2019 (ANFIA, Camera di Commercio di Torino, CAMI, Edizioni Ca’Foscari); www.investinemiliaromagna.eu; http://www.innovazioneautomotive.eu/polo-innovazione-automotive/; http://exemerge.disim.univaq.it/; www.investincampania.it; RIS3 Campania; https://clusterlucanoautomotive.it/; Outlook Report n. 1/2020 – Automotive, ARTI – Agenzia Regionale per la tecnologia e l’innovazione.
REGIONAL ECOSYSTEM
Italian automotive and engineering clusters
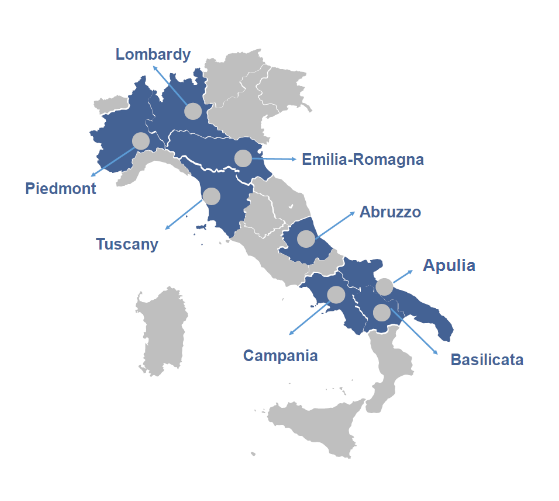 |
The automotive industry in Italy is defined by several production hubs spread throughout the country.
-
Piedmont: birthplace of FIAT (later merged in FCA and now Stellantis), the region is the forerunner in Italy in terms of automotive components companies and accounts for around 33% of the national automotive components industry.
-
Lombardy: 2nd region in Italy by number of automotive suppliers, counting on both international mega-suppliers and numerous small and medium-sized suppliers. 27% of the Italian automotive components industry is in this region.
-
Emilia-Romagna: known for the Motor Valley, where world-famous Italian luxury brands are produced. In fact, there is a high presence of sports cars and motorbikes companies like Ferrari, Lamborghini, Ducati, Maserati, Dallara, Pagani, Red Bull, FAW, etc., and high-level suppliers such as AVL, HPE Coxa, Marelli, Borg Warner etc.
-
Tuscany: here the automotive sector is made up of two groups: 1) large multinational, technology intensive, operating in the components sector; 2) high number of SMEs with limited or non-existent trend towards internationalization.
-
Abruzzo: the regional automotive supply chain is made up of a group of globalized companies, both Large and SMEs, operating in the automotive and mechatronics sector which also includes subcontracting and components. The supply chain is at the service of both four-wheeled and two-wheeled vehicles, thanks to the presence of the FCA Italy production site for light commercial vehicles (Stellantis group) and Honda Italia Industriale, the only Honda two-wheeler production site in Europe.
-
Campania: there is a relevant presence of production poles represented by large multinationals and small and medium-sized enterprises, operating both upstream of the supply chain, in the supply of materials, in processing and equipment, in the design and along the supply chain, in the design and testing of parts, in the construction of components and systems, in the specialized subcontracting of parts.
-
Basilicata: here the automotive sector revolves mainly around the Stellantis plant in Melfi, where the company plans to produce 5 new models belonging to the DS, Jeep, Lancia, and Opel brands starting from 2024. Over time, the presence of the Melfi plant contributed to the creation of a components industry, and today the automotive sector plays an important role in the regional economy.
-
Apulia: one of the strengths of the regional automotive supply chain is the availability of highly qualified and skilled workers, technicians and engineers, thanks to the important contribution in terms of training offered by the regional territory.
SUSTAINABLE AND SMART MOBILITY
The automotive industry boasts a long tradition in Italy, and is now experiencing a strong moment of change towards sustainable and smart mobility, driven by consumer preferences, public policies and incentives, public and private innovation and research.
In fact, there is a growing consumer interest in sustainable vehicles, which is also supported by national policies and incentives for purchasing low emission vehicles.
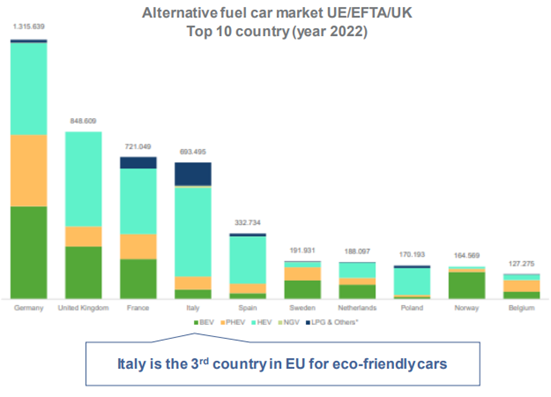 |
Sources: Osservatorio sulla componentistica automotive italiana 2022, ANFIA, Camera di Commercio di Torino; Focus UE/EFTA/UK mercato autovetture ad alimentazione alternativa, FY 2022, Area Studi e Statistiche ANFIA
A promising market is represented by connected cars: in 2022, it reached the value of €2,5 billion, and it is estimated to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 23,8% and to reach a value of over €9 billion by 2027.
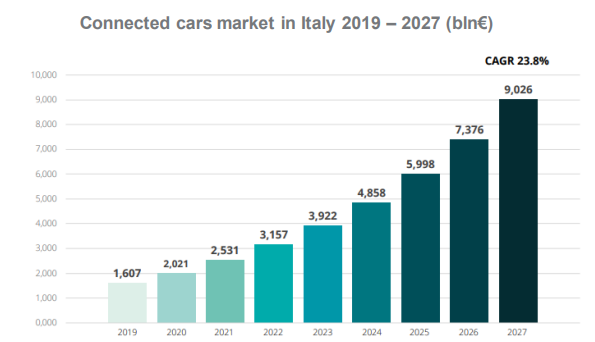 |
Source: Deloitte, Think Tank. Automotive White Paper 1. Una visione di filiera per la ripartenza strategica del settore
Another noteworthy phenomenon is the one of shared mobility, grown over the years: the number of shared vehicles has reached almost 113k units in 2022. The share of micro-mobility vehicles (push scooters, bicycles, scooters) on the total fleet in Italy exceeded 93% in 2022.
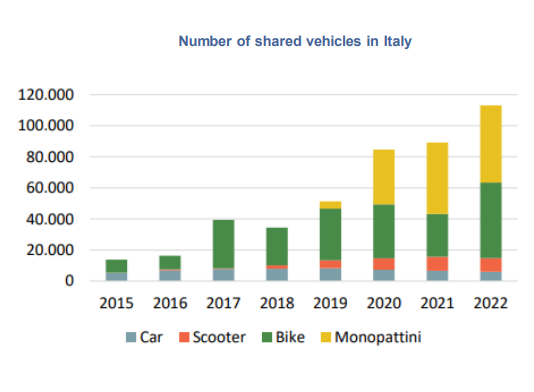 |
Source: 7° Rapporto nazionale sulla sharing mobility, Osservatorio Nazionale Sharing Mobility, 2023
The number of rentals has grown steadily over the years:
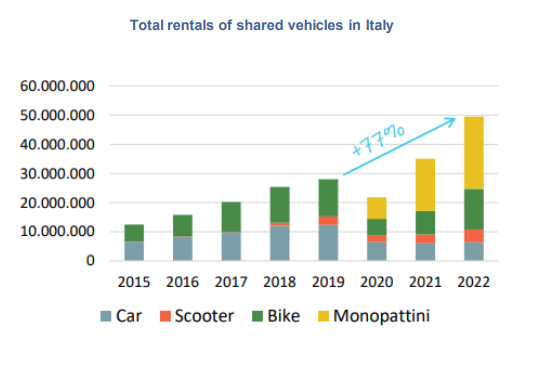 |
Source: 7° Rapporto nazionale sulla sharing mobility, Osservatorio Nazionale Sharing Mobility, 2023
ADVANCED AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGICAL ECOSYSTEMS
Italy ranks 2nd in the EU-27 and 7th worldwide by number of citations in automotive engineering:
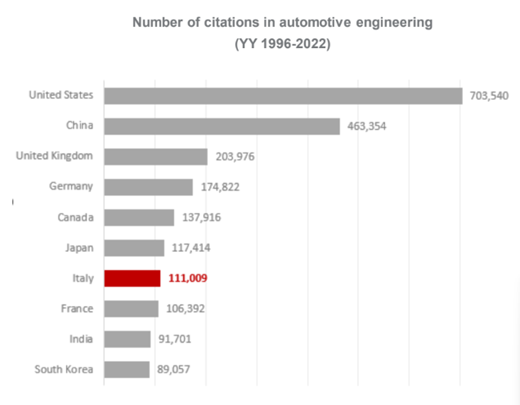 |
Sources: Istat NACE code 29 - Manufacture of motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers; Scimago Journal & Country Rank
The research activity takes place both at research centers distributed throughout the territory and at universities. In particular, among the main reference points, those that are noteworthy are: 1) the National Research Council (CNR), that is the largest public research institution in Italy; 2) the National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development (ENEA); 3) the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT); 4) Fondazione Bruno Kessler (Trento); 5) Torino CityLab, promoted by the City of Turin.
Research centers Hub&Spoke devoted to sustainable mobility:
-
SustainableMobility Technology Center (Turin)
-
Sustainable Mobility Center (Milan)
Universities with research activities in e-mobility:
 |
ACADEMIC ECOSYSTEM & TALENT POOL
As for the academic ecosystem, Italian universities rank among the best in the world in Engineering and Technology subjects. They also collaborate with automotive companies for the development of new technologies and for training activities.
 |
Source: QS World University Rankings by Subject 2023



