Italy is moving towards a clean energy transition through energy and climate policies. 40% of the National Recovery & Resilience plan (NRRP) funds are allocated to achieve Italy’s green and ecological transition by increasing the share of renewable energy sources, developing hydrogen, decarbonising hard to abate industries and moving towards sustainable mobility.
RENEWABLE ENERGY
Thanks to its geographical position, high availability of renewable energy sources and government commitment Italy is becoming a European energy hub.
2021 KEY FIGURES
|
|
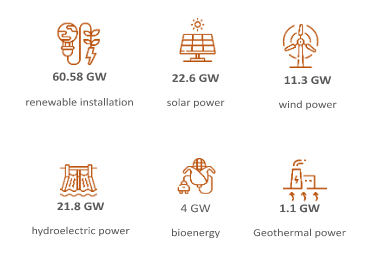
About 120 GW of additional RES capacity will be installed in Italy by 2030 with an expected remarkable increase in RES technologies demand in the next 10 years.
In recent years, the Italian government has implemented several incentive schemes to encourage the development of renewable energy production and adopted important regulatory measures (i.e. Simplification Decree, Energy Decree, RED II, etc) in order to ease, accelerate and streamline RES procedures and meet the environmental and energy goals.
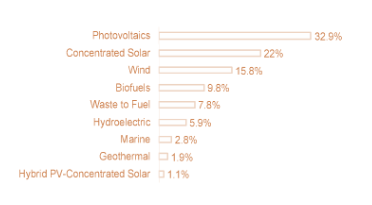
Italian RES patents - Breakdown for technological domains (% on total)
|
|
Italy has a prominent and innovative industrial base with 400 companies producing components for RES plants with a 23€ bln turnover and almost 60.000 direct employees. According to the last available statistics, around 1,200 Italian patents relating to RES technologies filed with the European Patent Office, mainly in the solar and wind energy domains.
AGRO-VOLTAIC SYSTEMS
The construction of agro-voltaic systems is among the initiatives promoted by the Italian government to guarantee a hybrid use of agricultural land for agricultural production and the production of electricity from RES. To access the incentives the PV systems must have rotating modules groud mounted and a monitoring system of crops and land. The NRRP and other decrees have introduced regulatory changes to simplify and incentivize it.
HYDROGEN
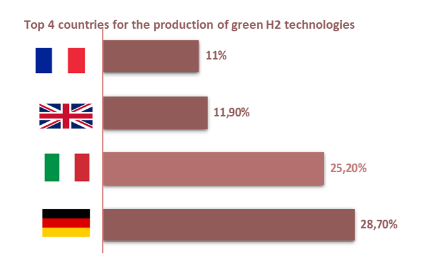
Since 2020 Italy launched a national hydrogen strategy to decarbonize the economy and meet European climate targets. The NRRP confirms the strategy with €3.19 bln for hydrogen focusing mainly on hydrogen production in dismissed industrial areas, pilot projects for hard-to-abate sectors, transportation and R&D investments. The positioning in the hydrogen supply chain show that Italy has a competitive advantage in various technological clusters and expertise in core and ancillary technologies that can be used for hydrogen.
|
|
HARD TO ABATE INDUSTRIES
The hard-to-abate sector is extremely relevant in Italy:
|
|
The HtA sector, responsible for 64% industrial direct CO2 emissions, is the main off-taker of technological solutions for decarbonization processes such as renewable energy sources, hydrogen and CO2 abatement technologies.
In order to decarbonize the Italian steel, paper, glass and ceramic industries will be needed at least:
|
|
TALENT POOL & INNOVATION ECOSYSTEM
Italy boasts a highly qualified and competititve talent pool, also thanks to the presence of some of the most renowned academic institutions in the world. Public research centers with advanced know-how in energy technologies are available for R&D partnership, while several science parks and industrial poles offer ideal infrastructures and networks for technology-intensive investments.
237K graduates in key subjects for the Green Transition over the last 3 academic years (2018-2020)
There are 8 Italian public Universities included in the top 250 QS World University ranking 2021 for highly competitive «Engineering & Technology» domain:

The Eco-Innovation Index 2021 of the European Commission shows that the national industrial ecosystem, with a positioning above the EU average, is committed to innovation for the ecological transition. Important players of the national R&D&I system are participating to the IPCEI programs (Important Projects Of Common European Interest) such as ENEA (Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development), which launched "flagship" initiatives: the new dedicated hi-tech laboratory for the battery supply chain and the Hydrogen Demo Valley.
Source: INVITALIA elaborations on data and information by The European House Ambrosetti & SNAM ; BCG; National Hydrogen Strategy Preliminary Guidelines; MIUR (Ministry of University and Research); QS World University Rankings; Enea.